Deformation mechanism maps provide a visual tool categorizing the dominant deformation mechanism as a function of homologous temperature shear modulus normalized stress and strain rate generally two of these three properties most commonly temperature and stress are the axes of the map while the third is drawn as contours on the map.
Stress vs strain curve ceramics vs metals.
After plotting the stress and its corresponding strain on the graph we get a curve and this curve is called stress strain curve or stress strain diagram.
With the sample geometry a stress strain curve can then be generated from the recorded load and displacement.
A highly elastic polymer may stretch over 10 times the original length before breaking while a metal might elastically stretch 10 of the original length elastically and may stretch.
The elastic deformation of a solid is a reversible process when the applied stress is removed the solid returns to its original state.
With a very short elastic region but highly capable of supporting huge stresses.
To populate the map constitutive equations are found.
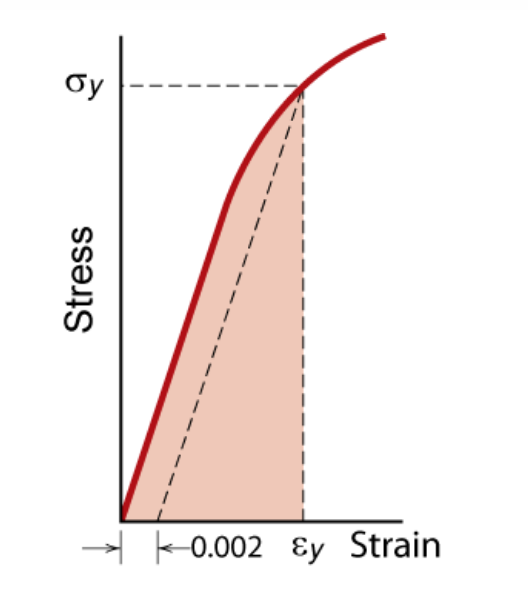
While some of the stress strain curves for polymers might look similar to ones for metals polymers are mechanically different than metals or ceramics.
Elastomers are the ones that strains more w a lower stress.
1 metals al alloy stress strain curve.
Stress and strain are linearly related and.
After the point d the material due to strain hardening again starts taking load and the curve rises as seen in the.
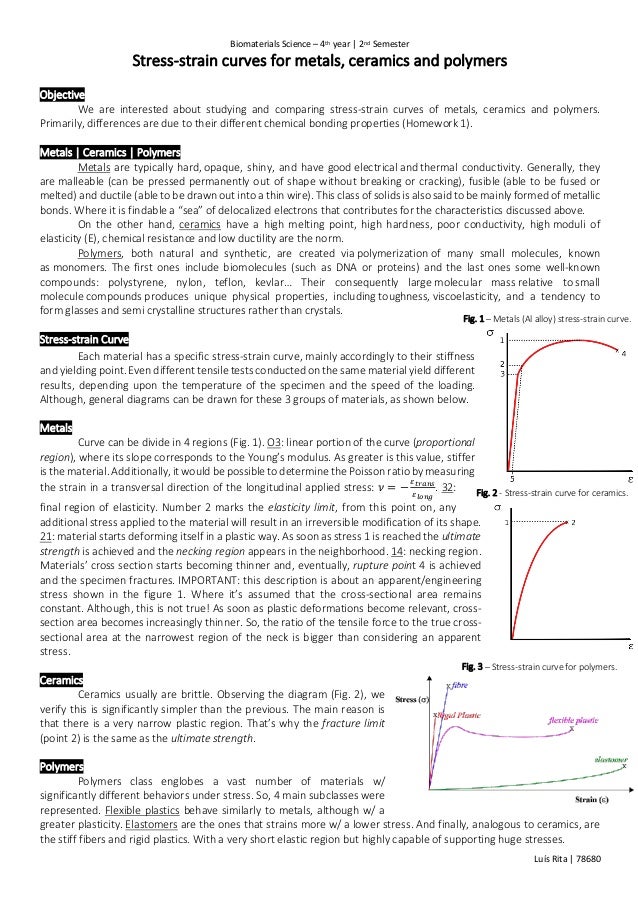
When the plot of stress versus strain is linear the system is said to be in the elastic state.
2 stress strain curve for ceramics.
Derived from axially loading an object and plotting the stress verses strain curve.
The zone where a material will return to its original shape for a given amount of stress toe region applies to a ligaments stress strain curve.
Stress strain curve is the plot of stress and strain of a material or metal on the graph.
And finally analogous to ceramics are the stiff fibers and rigid plastics.
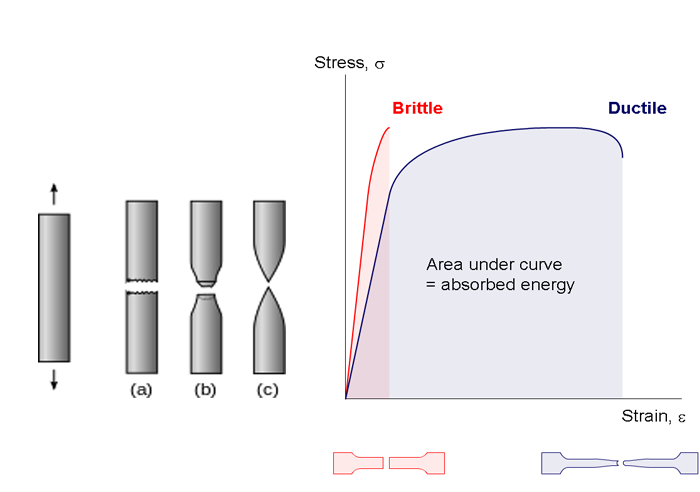
A typical stress strain profile for a ductile metal resembles the following.
However when the stress is high the plot passes a small jump on the axes.
Represents straightening of the crimped ligament fibrils.
Stress vs strain curve.
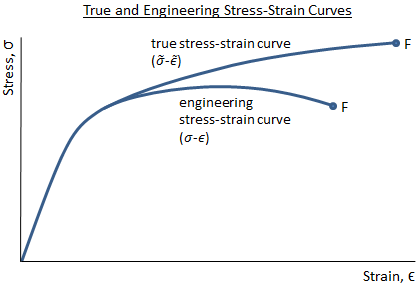
In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain it is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing these curves reveal many of the properties of a material such as the young s modulus the yield strength.
In this the stress is plotted on the y axis and its corresponding strain on the x axis.
Yielding starts at c and ends at d.
Stress strain curves for two brittle materials.